Insight
13 Sep. 2022
Ideation: The Keys to an Effective Process to Promote Innovation
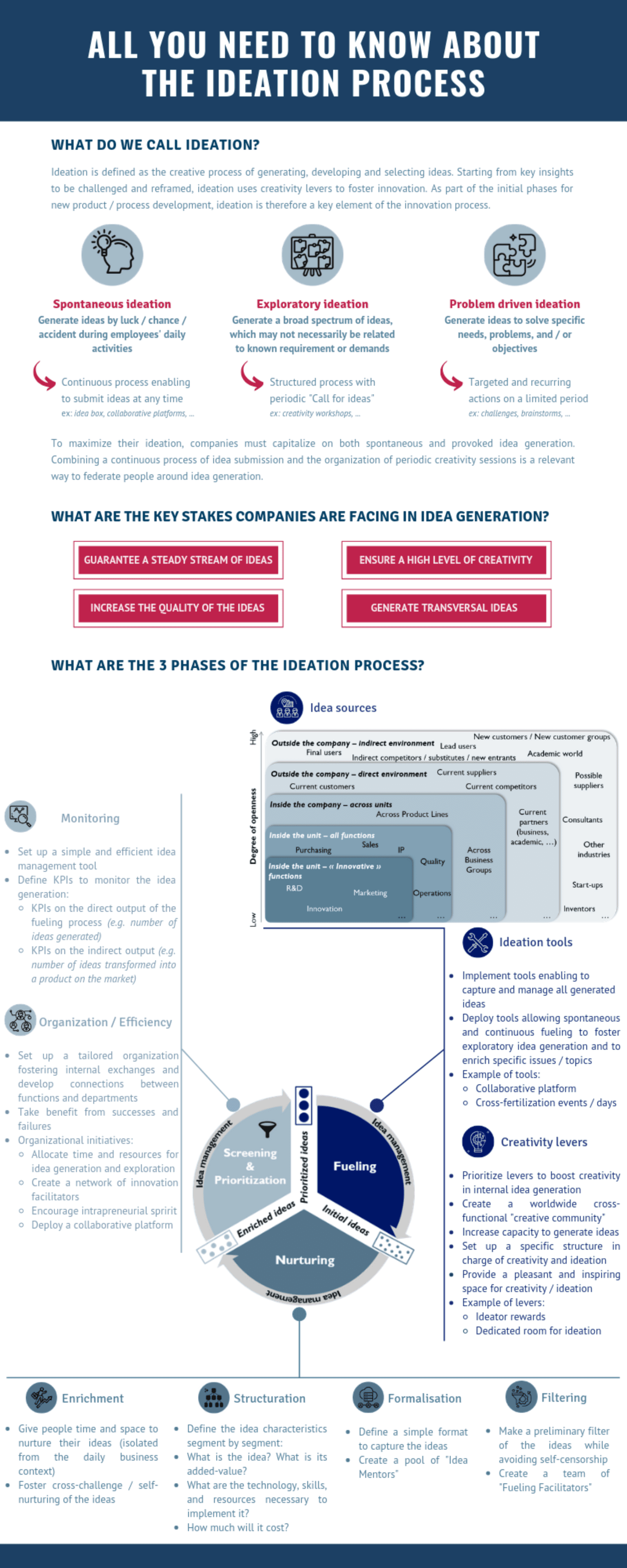
Ideation is defined as the creative process of generating, developing, and selecting ideas. Starting from key ideas to be questioned and reframed, ideation uses levers of creativity to promote Innovation. As part of the initial development phases of new products or processes, ideation is therefore a key element of the process in place within the Research, Innovation and Development department.
The 3 Types of Ideation at Work in Organizations
Spontaneous Ideation
Generate ideas by chance / accident / accident during daily activities of employees.
- Continuous process allowing ideas to be submitted at any time, for example: suggestion box, collaborative platforms …
Exploratory Ideation
Generate a wide range of ideas, which are not necessarily related to known requirements or demands.
- Structured process with periodic “calls for ideas”, example: creativity workshops.
Ideation Guided by a Problem
Generate ideas to solve specific needs, problems and / or goals.
- Targeted and recurring actions over a limited period, example: challenges, brainstormings …
To maximize their ideation, companies must capitalize on spontaneous and provoked idea generation. Combining an ongoing process of idea submission and the organization of periodic creativity sessions is a relevant way to unite people around idea generation.
The key Challenges for Companies in Relation to the Generation of Ideas
- Guarantee a constant flow of ideas
- Ensure a high level of creativity
- Increase the quality of ideas
- Generate transversal ideas
The Three Phases of the Ideation Process and Associated Advice
Phase 1: Generation of Ideas
Implementation of Tools to Capture and Manage All the Ideas Generated:
- Deploy tools allowing spontaneous and continuous feeding to promote the generation of exploratory ideas and enrich specific issues / subjects
- Example of tools: collaborative platform & cross-fertilization events / days
Levers to Boost Creativity in the Generation of Ideas Internally:
- Creation of a transversal “creative community”,
- Implementation of a specific structure in charge of creativity and ideation,
- Provision of a pleasant and inspiring space for creativity / ideation Example of levers:
- Example: rewards for the ideator and room dedicated to ideation
Phase 2: Maturation of Ideas
Enrichment
Give people time and space to nurture their ideas (isolated from the daily business context)
- Foster cross-challenges / self-development of ideas
Structuring
Define the characteristics of the idea segment by segment:
- What’s the idea?
- What is its added value?
- What are the technology, skills and resources needed to implement it?
- What will the cost be?
Formalization
Define a simple format to capture ideas:
- Create a pool of “Idea Mentors”
Filtering
Make an initial filtering of ideas while avoiding self-censorship:
- Create a team of “Ideation Facilitators”
Phase 3: Selection and Prioritization
Monitoring
Set up a simple and effective idea management tool:
- Define KPIs to monitor idea generation:
- KPI on the direct output of the feeding process (for example, number of ideas generated),
- KPI on indirect output (for example, the number of ideas turned into a product in the market).
Organization / Efficiency
Set up a tailor-made organization promoting internal exchanges and developing links between functions and services:
- Take advantage of successes and failures,
- Promote organizational initiatives:
- Allocate time and resources to the generation and exploration of ideas,
- Create a network of innovation facilitators,
- Encourage the intrapreneurial spirit,
- Deploy a collaborative platform.
Infographics